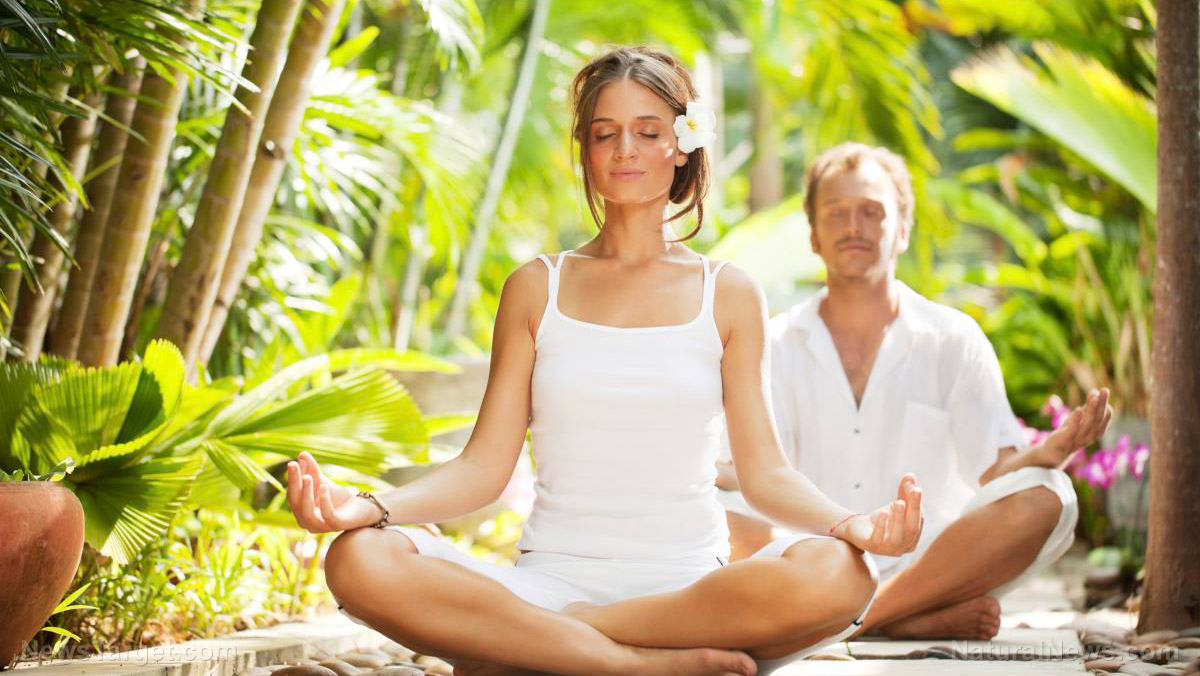
Controlled yogic breathing found to effectively reduce stress-induced disorders
10/19/2018 / By Ellaine Castillo

Constantly being stressed is not good for the body. It can result in disorders, such as anxiety and depression, that could be disabling to the affected individual. A study, published in the Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, looked at the potential use of yogic breathing practice, Shambhavi Mahamudra Kriya, as a treatment for stress-induced disorders.
- Many cases of adult disability are due to stress-induced disorders. These include mood disorders that are caused by a complex network of factors like stress, oxidative stress, inflammation, and hormonal response.
- Additionally, constant stress can also worsen cardiovascular diseases, obesity, mental health, gastrointestinal problems, and sleep disorders.
- Previous studies have shown that meditation and yoga practices have great potential in the treatment of stress-induced mood disorders. However, no studies have been conducted regarding the specific effect of Shambhavi Mahamudra kriya on stress-induced disorders.
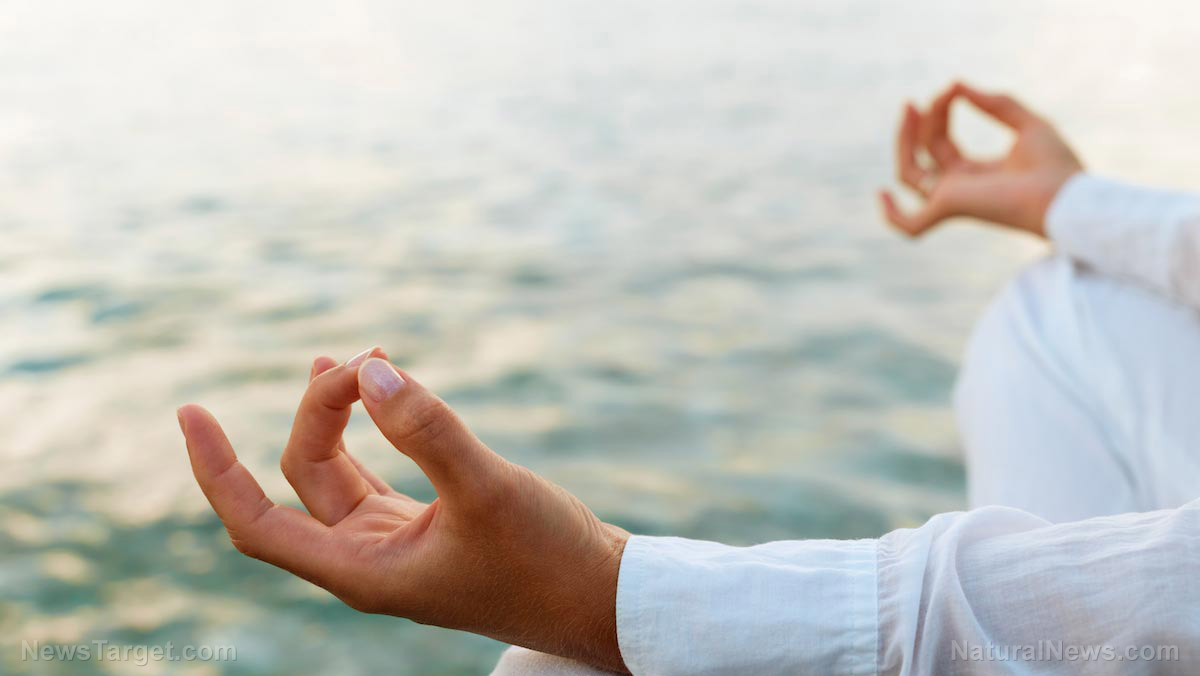
- Shambhavi Mahamudra kriya is a practice that integrates yogic breathing (pranayama) and meditation.
- The participants for this study performed a 21-minute long Shambhavi Mahamudra kriya routine on a daily basis for a period of six weeks. Afterward, they were asked to evaluate their levels of perceives stress and general well-being.
Overall, the participants of the study experienced lower levels of perceived stress while their feelings of general well-being improved. These prove that Shambhavi Mahamudra kriya can serve as an alternative therapy for stress-induced mood disorders.
Read the full text of the article at this link.
Learn more about the effects of yoga on stress-induced disorders by visiting Mental.news today.
Journal Reference:
Peterson CT, Bauer SM, Chopra D, Mills PJ, Maturi RK. EFFECTS OF SHAMBHAVI MAHAMUDRA KRIYA, A MULTICOMPONENT BREATH-BASED YOGIC PRACTICE (PRANAYAMA), ON PERCEIVED STRESS AND GENERAL WELL-BEING. Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine. 13 August 2017;22(4). DOI: 10.1177/2156587217730934
Tagged Under: alternative therapy, Anxiety, Ayurveda, calm, chronic stress, depression, Meditation, mental health, mood, mood disorder, pranayama, Shambhavi Mahamudra, stress, stress-induced disorder, therapy, Yoga, yogic breathing